Java 中的 findFirst 流方法 D栈 Delft Stack

Java Stream API — Learn how to convert streams to other data structures by tech.mia
The findFirst method of Stream finds the first element as Optional in this stream. If stream has no element, findFirst returns empty Optional. If the stream has no encounter order then findFirst may select any element. If the selected element by findFirst is null, it throws NullPointerException . Find the findFirst declaration from Java doc.

Java Stream Findfirst Explanation With Example Codevscolor Riset
Stream findFirst () in Java with examples Read Courses Practice Stream findFirst () returns an Optional (a container object which may or may not contain a non-null value) describing the first element of this stream, or an empty Optional if the stream is empty. If the stream has no encounter order, then any element may be returned. Syntax :

Convertir lista a map en Java Delft Stack
List

Java之Stream流_stream流findfirstCSDN博客
The Stream findFirst () method returns an Optional describing the 1st element of the stream, or an Optional, which has to be empty if the stream is empty. Syntax: Optional

10 Examples of Stream Class in Java 8 [ map + filter+ flatmap + collect + findFirst ]
In this guide, you will learn about the Stream findFirst() method in Java programming and how to use it with an example.. 1. Stream findFirst() Method Overview. Definition: The Stream.findFirst() method is a terminal operation that returns an Optional describing the first element of the stream, or an empty Optional if the stream is empty.. It is particularly useful in parallel streams where it.

10 Reasons why Java is better than JavaScript Incentergy Effizienzsteigerndes Projektmanagement
Find first element by predicate Asked 9 years, 7 months ago Modified 1 year, 10 months ago Viewed 608k times 693 I've just started playing with Java 8 lambdas and I'm trying to implement some of the things that I'm used to in functional languages.

Java 中的 findFirst 流方法 D栈 Delft Stack
The findFirst method returns an Optional describing the first element of a stream, or an empty Optional if the stream is empty. The findAny method returns an Optional describing some element of a stream, or an empty Optional if the stream is empty. Java Stream findFirst example In the next example we use the findFirst method.

Difference between findAny and findFirst of Java Stream API CodeVsColor
2. Parallel findFirst () String result is = Putin. 3. filter name starting with 'M' & findFirst () result is = Manmohan. 4. names starting with 'A' = Optional.empty. . 3. Stream findAny () method : This Stream method is a terminal operation which returns Optional instance describing any element from the given Stream.
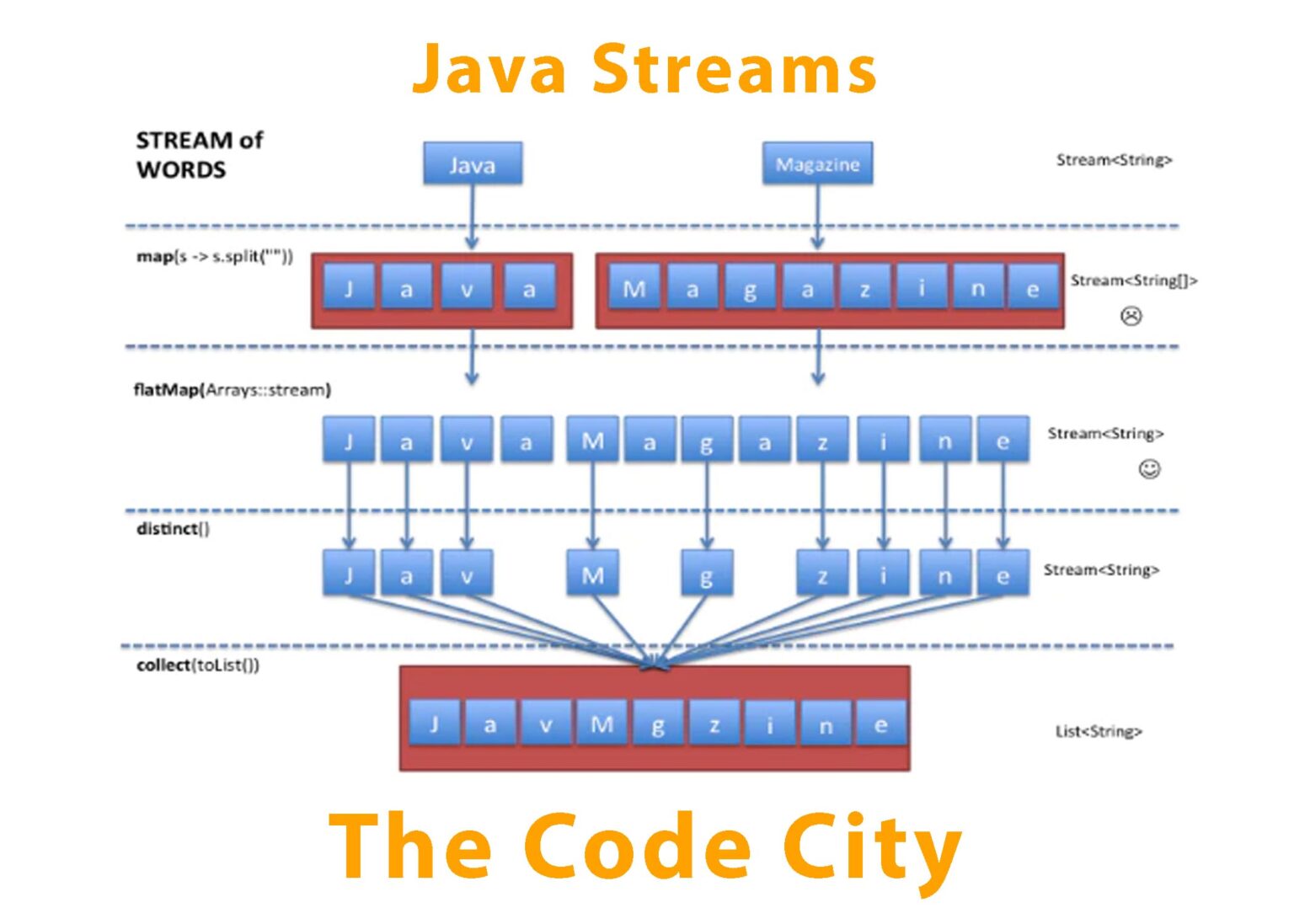
Streams in Java Quick Guide with Examples The Code City
1. Overview The Java 8 Stream API introduced two methods that are often misunderstood: findAny () and findFirst (). In this quick tutorial, we'll look at the difference between these two methods and when to use them. Further reading: Filtering a Stream of Optionals in Java
Java Stream Findfirst Explanation With Example Codevscolor Riset
The findFirst () method returns the first element of a stream or an empty Optional. If the stream has no encounter order, any element is returned, as it's ambiguous which is the first one anyway. The findAny () method returns any element of the stream - much like findFirst () with no encounter order. Use Cases of findFirst () and findAny ()

Java之Stream流_stream流findfirstCSDN博客
A sequence of elements supporting sequential and parallel aggregate operations. The following example illustrates an aggregate operation using Stream and IntStream : int sum = widgets.stream () .filter (w -> w.getColor () == RED) .mapToInt (w -> w.getWeight ()) .sum (); In this example, widgets is a Collection

Java 8 Stream findFirst vs. findAny Perfomance and Functional Differences Pedro Lopes
Java stream findFirst() explanation with example: findFirst() is used to find the first element in a stream in Java.It returns one Optional value holding the element found. If the stream is empty, it will return one empty optional. In this post, I will show you how findFirst() works with an example.. Definition of findFirst:

Is Java Compiled or Interpreted Programming language?
1. Stream findFirst () method 1.1. Description Optional

Java 8 Streams YouTube
The findFirst () method returns an Optional describing the first element of the given stream if Stream is non-empty, or an empty Optional if the stream is empty. 1. Stream findFirst () Method Optional

Java 8 Stream findFirst vs findAny examples Techndeck
The Stream findFirst () method is used with streams to retrieve the first element of the stream, assuming an order exists for the stream (for example, a list maintains its order, so findFirst () will return the first element of the list). If the stream is empty, it will return an empty Optional. Syntax for findFirst () method

Java Stream map() vs flatMap() Example Codez Up
Main similarity is findFirst () and findAny () method returns the first value from the stream if it is sequential. By default, stream is created with sequential pattern. And always both methods returns the same value. if the any value in the stream is null then it will throw NullPointerException. But, if you working with parallel streams and.